Chlamydia trachomatis is the bacterium responsible for producing a common type of STD known as Chlamydia. It falls into the category of the “most common infection to be transmitted via sexual means”.
Chlamydia treatment should be carried out in its early stages before the infection goes fatal. The condition may go symptomless in 75% of affected women, and in about 50% of affected men.
How is it transmitted?
This bacterium can easily be transferred among sexual partners through oral, vaginal or anal sex methods. Chlamydia can even be passed on from an infected mother to her baby during child birth.
What are the signs and symptoms?
As mentioned earlier, that the disease remains clueless in more than half of the infected cases. However, its spread within the body is fast and must be eradicated immediately.
Amongst the asymptomatic female population, about half of them are observed to develop symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID relates to inflammation and scarring of the pelvic reproductive organs, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubules and uterus. PID can end up with serious consequences if not treated in early stages. Untreated PID can cause infertility. In men, the disease can cause epididymitis, which can lead to sterility if not resolved soon.
Some infected cases may show general signs of an STD infection, such as abnormal genital discharge, pain, redness or rash in the genital area, fever and urinary urgency.
Chlamydia conjunctivitis is yet another symptom which once used to be an important cause of blindness worldwide.
This STD can cause premature conjunctivitis and blindness in infants, who catch the infection during their birth process. The disease can also produce spontaneous abortion.
Chlamydia can also involve joints, producing ‘reactive arthritis’.
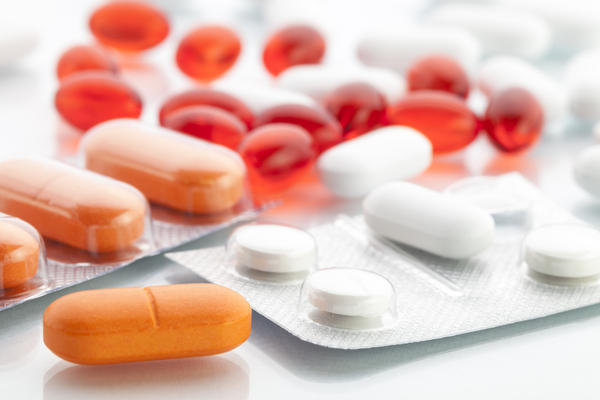
How is it treated?
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment of Chlamydia. A variety of such medicines can be employed in its treatment such as Doxycycline, Azithromycin, Ofloxacin and Erythromycin. Pregnant women infected with Chlamydia are treated with Amoxicillin or Erythromycin, as other antibiotics may cause harm to the developing fetus.
In most cases, doctors prescribe a seven-day course for the treatment. It is highly advised to abstain from sexual activity during this period so as to avoid spread of infection to the partner. Proper and complete treatment is necessary so as to avoid re-infection, which is fairly common.
One can also buy chlamydia tablets following a reliable web source, which also offers Chlamydia testing kit for the purpose of obtaining confirmed results.


























No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel