The word apnea has a Greek origin. It is taken from the word “apnous” or “apnoia” that means “breathless”. Sleep apnea greatly decreases your sleep quality.
As a result of which your overall health also takes a corresponding decline. If you regularly suffer from tiredness in the morning after all night’s sleep and your bed partner nags about ‘you snoring all night long’, you may be suffering from sleep apnea symptoms.
What is Sleep Apnea?
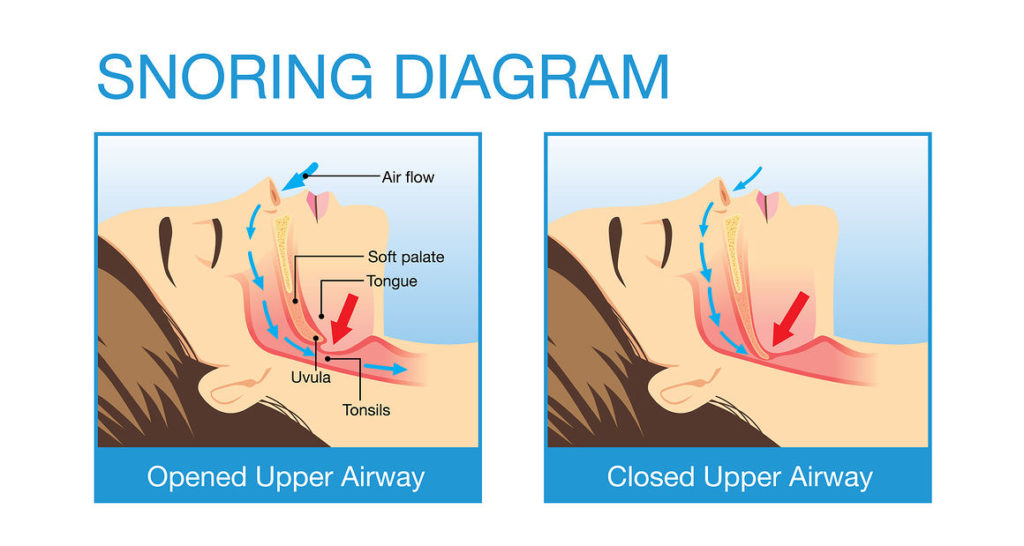
Sleep apnea is a condition where one’s breathing is interrupted during sleep. The phase lasts for a few seconds to a minute but is repeated unlimited times during the night. It is an involuntary act that does not cause the patient to wake up. Some patients may exhibit periods of shallow breathing rather than complete respiratory cessation.
An episode of apnea follows loud snoring and ends in a snort like noise. As the quality of sleep is disturbed, the patient suffers from daytime sleepiness and is often sullen and irritated. Sleep apnea symptoms in children reveal as hyperactivity and disturbed behavior in school. The reason behind this is very logical. Your brain and body do not get enough oxygen while sleeping.
How Common is Sleep Apnea?

Sleep apnea symptoms may be found in both sexes and all ages including children. Sleep apnea affects more than 18 million adults in the US. One out of every five individual suffers from mild symptoms of sleep apnea while one in fifteen suffers from moderate to severe symptoms.
An estimated minimum of 2-3% prevalence is found in children. The figure rises to 10-20% in children with habitual snoring.
Causes of Sleep Apnea in Adults
Based upon the root cause, sleep apnea is categorized as
- Central sleep apnea
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Mixed type, also called treatment-emergent central sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type. It occurs when the throat muscles are lax and airway gets blocked by soft tissue. Thickened soft tissue or excessive fat may also act as obstructive agents
Central sleep apnea occurs when there is a disturbance in the signaling from the brain respiratory center. The respiratory muscles fail to act when they do not receive the signal. The rhythm and control do not synchronize in central type. This type is usually associated with the underlying condition as heart failure, stroke, and use of certain pain medications.
The mixed type, as the name indicates, defines a condition where both central and obstructive types exist in parallel.
How Do You Know if You Have SleepApnea Symptoms?
The symptoms of sleep apnea defining the obstructive and central types usually overlap. A sleep study distinguishes between the two. Some of the common symptoms of sleep apnea in adults include
- Episodes of breathing interruption or stoppage, often informed by the bed partner or spouse
- Loud snoring, which is much more disturbing to the bed partner
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Dry mouth
- Interrupted sleep with difficulty staying asleep(insomnia)
- Increased frequency of urination at night
- Early morning headaches
- Day time sleepiness
- Lack of focus during the day
- Irritable and prickly behavior
How Do You Know Your Kid Suffers from Sleep Apnea Symptoms?
[su_highlight background=”#fed388″]Did you know children often get misdiagnosed with ADHD instead of sleep apnea? That is because children do not fit the typical patient sketch of sleep apnea.[/su_highlight]
Though the symptoms of sleep apnea almost remain the same, the day-time symptoms resemble that of the hyperactivity associated with ADHD. That is why it is important to keep a vigilant check on sleep apnea symptoms in children.
About 10% of children with complaints of snoring suffer from sleep apnea.
- Mouth breathing
- Daytime sleepiness
- Poor concentration and short attention span
- Behavioral problems
- Sluggish performance at school
- Bedwetting
- Sleep terrors
- Causes of sleep apnea in children
The causes of sleep apnea in children invariably includes the obstructive type. Most often, the obstruction is caused by enlarged adenoids or tonsils. Childhood obesity is another reason that acts as a risk factor for sleep apnea. Children with Down’s syndrome often present with sleep apnea.
[su_highlight background=”#fed388″]The throat muscles become relaxed while sleeping. The soft tissue and enlarged adenoids or tonsils obstruct the airway resulting in snoring and episodes of sleep apnea.[/su_highlight]
Risk Factors for Sleep Apnea
Certain risk factors make you more prone to the development of sleep apnea. These are stated as
Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Being overweight or obese
Being overweight imposes fat deposits in your neck, making the airway narrower.
- A narrow airway
Any obstruction, be it fat deposits or enlarged thyroid or tonsils particularly in children predisposes to sleep apnea symptoms.
- Nasal deformity like DNS
Nasal deformity like a nasal septum causes congestion in the nose making the airway narrow.
- Allergy or sinusitis
Any kind of allergy, particularly chronic allergic conditions as sinusitis poses a risk for sleep apnea in the long-term.
- Neck circumference
A neck circumference of 17 inches or more in men and 15 inches or more in women is a risk factor for the development of sleep apnea.
- Gender
Men are two to three time more likely to suffer from sleep apnea. It is a clinical observation.
- Age
As we grow old, our muscles lose their tone. Flabby and slack neck muscles predispose to sleep apnea.
- Family history
Sleep apnea might run in the family.
- Use of certain medications
Sedatives and tranquilizers relax the throat muscles making you more prone to developing sleep apnea with extended use.
- Excessive use of alcohol
Alcohol works the same way as relaxant drugs.
- Smoking
Smoking increases the process of congestion in the upper airways by causing inflammation. Smokers are said to be three times more susceptible to sleep apnea symptoms.
- Menopause
Women have an increased risk of developing sleep apnea with the advent of menopause, an aging factor.
- Sleeping on your back
Risk Factors for Central Sleep Apnea
- Old Age
- Gender, men are more susceptible to central sleep apnea
- Cardiovascular disorders, especially congestive heart failure is a risk factor for central sleep apnea
- Stroke may cause damage to neck muscles thereby increasing the risk for sleep apnea or the mixed type
- Certain long-acting medications as opioid pain killers raise the risk for central sleep apnea
Risk Factors in Children
- Downs syndrome
- Congenital defects in the skull or face
- History of low birth weight
- Cerebral palsy
- Sickle cell disease
- Neuromuscular disorder
- Family history of obstructive sleep apnea
Long-term Complications of Sleep Apnea Symptoms
The ideal situation is to diagnose sleep apnea symptoms promptly and receive treatment. Sleep apnea symptoms if allowed to be continued without treatment cuts down the quality of life. It also culminates into many other life-threatening conditions. Some of the complications of untreated sleep apnea include
Complications in Adults
- Fatigue and low energy reserves
- High blood pressure
- Heart ailments
- Metabolic syndrome
- Diabetes Type II
- Liver disease
- Complications of surgery
- Complications of medicines
- Heartburn
- Lack of energy
- Increased forgetfulness
- Decreased sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Sleep deprivation in one’s bed partner
Complications in Children
Some of the complications as lack of focus, day time sleepiness, poor school performance, disturbed behavior in children are common to adults. However, children may develop serious complications as
- Failure to thrive or grow
- Impaired cognitive development
- Heart ailments
- Death
Managing Sleep Apnea Symptoms in Children and Adults
For cases with mild symptoms, the underlying cause is usually addressed. Losing weight, quitting smoking, receiving prompt treatment for allergies are some.
Similarly, removal of adenoids or tonsils in children helps. Addressing the allergies with nasal decongestants and topical nasal steroid drops may help.
The common form of intervention therapy for both children and adults includes
-
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
CPAP is a machine that clears open the airways via delivering positive pressure through a mask. Though cumbersome in the beginning, most patients learn to sleep through the night with the help of this machine. With the advancement in technology, many upgraded versions of CPAP have emerged. They increase the user-compliance of the machine.
With the latest CPAP machine, side effects are less. Auto-CPAP and BPAP automatically adjust the air pressure during the inspiration and expiration phases. CPAP remains the most common remedy for sleep apnea so far.
-
Oral Devices
In cases of mild sleep apnea symptoms, oral devices are useful adjuncts. They move your jaw forward, thereby opening the throat and the nasal passages. These include dental devices and mouthpieces.
-
Surgery
If CPAP fails to deliver results after a three-month test and trial period and no other method brings the patience compliance up, then doctors often recommend surgery.
Surgery remains the first option in patients with a congenital deformity of the face or skull. Similarly, surgical removal of adenoids and tonsils in children greatly aids the symptoms of sleep apnea. Different forms of surgery include
- Tissue removal
- Tissue shrinkage (radiofrequency ablation)
- Implants into the soft palate
- Jaw rearrangement
- Stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve
- Tracheostomy in severe cases
Take Home Message
Sleep apnea symptoms may be confused with other breathing disorders and therefore are disregarded as a trivial issue. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment help avoid complications which may prove grave in pediatric cases. Long-term complications in adults can also be prevented thereby improving the quality of life.





























No Comments
Leave a comment Cancel